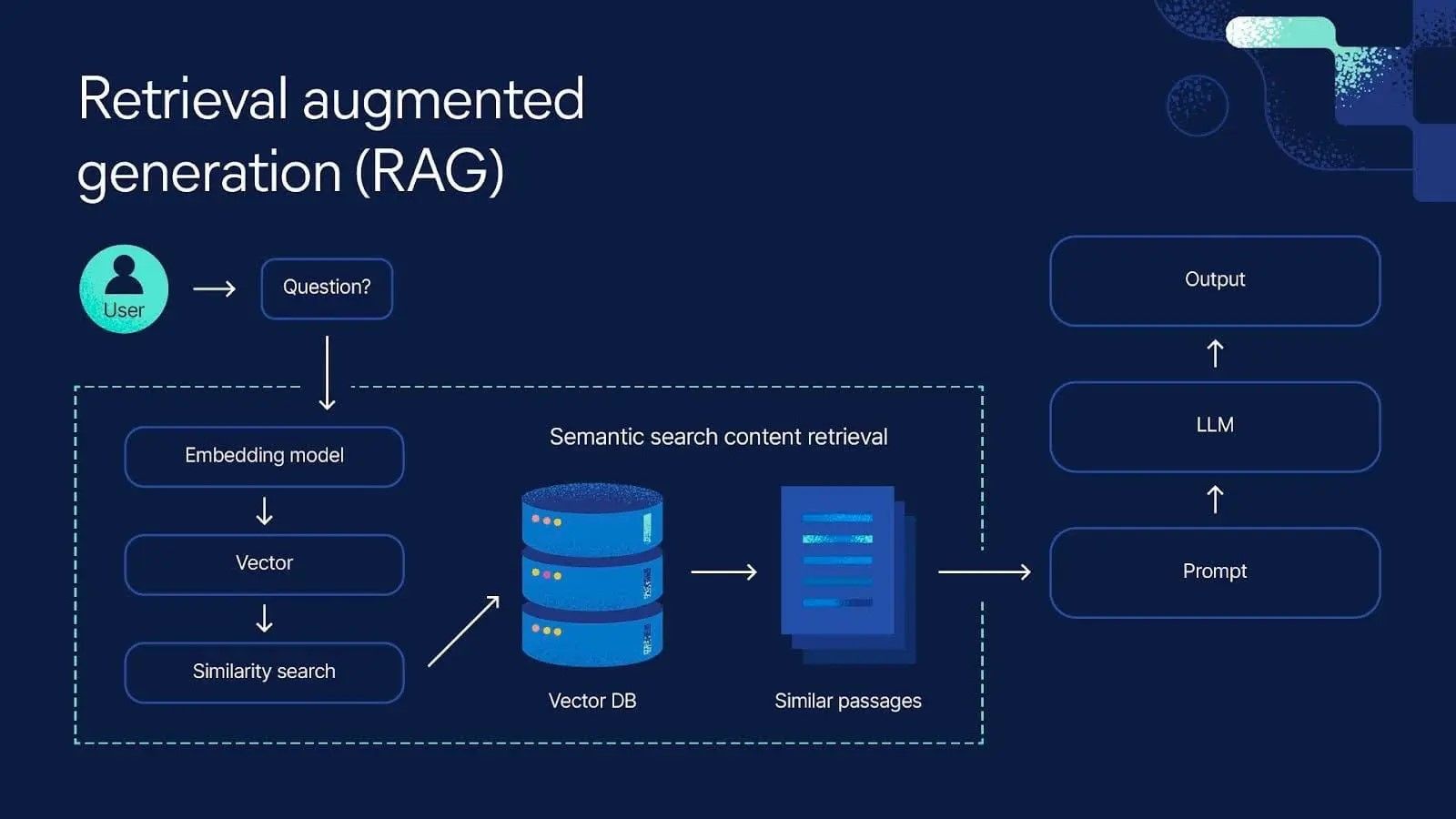
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for building more accurate and contextually relevant AI systems. However, evaluating RAG systems presents unique challenges that require specialized metrics and methodologies. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental concepts, key metrics, and best practices for effectively measuring RAG performance.
Understanding RAG Evaluation
RAG evaluation differs significantly from traditional language model evaluation because it involves two distinct components: retrieval and generation. Each component requires specific metrics, and their interaction adds another layer of complexity to the evaluation process.
Key Insight: Effective RAG evaluation requires measuring not just the final output quality, but also the retrieval relevance and the model's ability to synthesize retrieved information coherently.
Core RAG Evaluation Metrics
RAG evaluation encompasses three primary dimensions: retrieval quality, generation quality, and end-to-end performance.
Retrieval Metrics
- Precision@K: Measures the proportion of relevant documents in the top K retrieved results.
- Recall@K: Evaluates how many relevant documents are captured in the top K results.
- MRR (Mean Reciprocal Rank): Assesses the ranking quality of retrieved documents.
Generation Metrics
- BLEU/ROUGE: Traditional text similarity metrics for reference-based evaluation.
- BERTScore: Semantic similarity using contextual embeddings.
- Factual Consistency: Measures alignment between generated content and source documents.
End-to-End Metrics
- Answer Relevance: Evaluates how well the final answer addresses the original question.
- Context Utilization: Measures how effectively the model uses retrieved information.
- Groundedness: Assesses whether generated answers are supported by retrieved context.
Evaluation Methodologies
- Component-Wise Evaluation: Evaluate retrieval and generation components separately to identify specific performance bottlenecks.
- Human Evaluation: Human assessors evaluate outputs for relevance, accuracy, and coherence. While the gold standard, this approach is expensive and time-consuming.
- Automated Evaluation: Use LLM-based judges (like Root Judge) to automatically assess RAG outputs at scale. This offers consistency and efficiency.
- Multi-Turn Evaluation: Assess RAG performance in conversational contexts where information needs to be maintained across exchanges.
Best Practices for RAG Evaluation
Dataset Construction
- Create diverse test sets covering different domains and question types.
- Include both factual and reasoning-based questions.
- Ensure proper ground truth annotations for retrieval and generation.
- Account for multiple valid answers and retrieval paths.
Metric Selection
- Choose metrics aligned with your specific use case and requirements.
- Combine multiple metrics for comprehensive assessment.
- Consider both automatic and human evaluation approaches.
Evaluation Framework
- Implement continuous evaluation pipelines for ongoing monitoring.
- Establish baseline performance benchmarks.
- Create ablation studies to understand component contributions.
Common Evaluation Challenges
- Ground Truth Availability: RAG evaluation often suffers from lack of high-quality ground truth data.
- Metric Alignment: Traditional metrics may not capture the nuanced quality aspects of RAG outputs.
- Disentangling Components: Poor retrieval can limit generation quality, while poor generation can waste good retrieval.
Advanced Evaluation Techniques
- Counterfactual Evaluation: Assess how RAG systems perform when key information is deliberately removed or modified.
- Temporal Evaluation: Evaluate RAG performance over time as knowledge bases evolve.
- Adversarial Testing: Test RAG robustness against misleading or contradictory information in the retrieval corpus.
Implementing RAG Evaluation
Begin with simple metrics like retrieval precision and answer relevance, then gradually incorporate more sophisticated evaluation measures as your system matures.
- Define clear evaluation objectives and success criteria.
- Build comprehensive test datasets.
- Implement automated evaluation pipelines.
- Establish regular evaluation cycles.
Conclusion
RAG evaluation is a multifaceted challenge that requires careful consideration of retrieval quality, generation performance, and end-to-end system effectiveness. By implementing comprehensive evaluation strategies, teams can build more reliable and effective RAG systems.